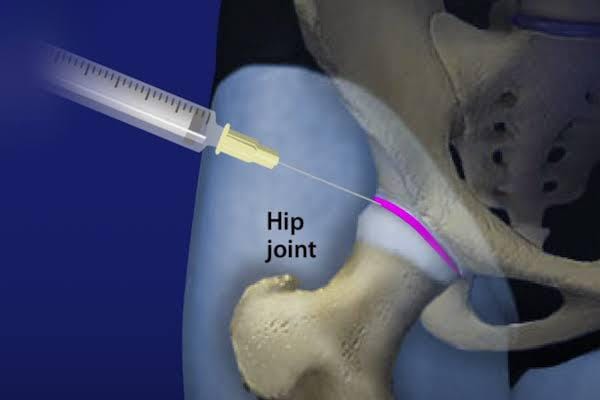
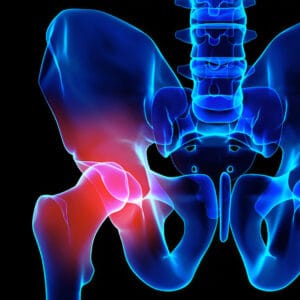
Hip Pain Treatment at RS Pain Management Clinic
Hip pain is a common condition that can affect people of all ages. It can arise due to various reasons, ranging from acute injuries to chronic conditions. The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint that supports the body's weight and allows for a wide range of motion. When affected, it can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
Signs and Symptoms of Hip Pain
- Pain Location: Discomfort in the groin, outer hip, thigh, or buttocks.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the hip joint, especially in the morning.
- Swelling and Tenderness: Around the hip joint.
- Limping: Difficulty walking due to pain.
- Radiating Pain: Pain traveling to the lower back, thigh, or knee.
- Snapping or Clicking Sounds: May be felt or heard during movement.
Common Causes of Hip Pain
1. Acute Injuries
- Fractures: Common in elderly individuals due to osteoporosis.
- Dislocations: Can occur from high-impact injuries like falls or accidents.
- Muscle Strains or Tendon Injuries: Resulting from overuse or sudden movements.
2. Chronic Conditions
- Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of cartilage in the hip joint.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Autoimmune inflammation of the joint.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: A type of arthritis causing stiffness and pain in the spine and hips.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa (fluid-filled sacs) that cushion the hip joint.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons around the hip joint.
- Labral Tear: Damage to the cartilage surrounding the hip socket.
- Avascular Necrosis (AVN): Bone tissue death due to lack of blood supply.
- Sciatica: Nerve compression causing radiating pain in the hip.
3. Other Causes
- Post-Surgical Pain: Pain after hip replacement or other surgeries.
- Mechanical Issues: Such as leg length discrepancy or misalignment.
- Infections: Septic arthritis or osteomyelitis (bone infection).
Diagnosis
To determine the cause of hip pain, the following diagnostic methods may be used:
- Physical Examination: Assessing range of motion, pain points, and joint stability.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-Rays: To check for fractures, arthritis, or bone abnormalities.
- MRI/CT Scans: For detailed imaging of soft tissues, such as cartilage and tendons.
- Ultrasound: To evaluate inflammation or fluid accumulation.
- Blood Tests: To identify infections or autoimmune conditions.
Treatment Options for Hip Pain
1. Medications
- Pain Relievers: NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Muscle Relaxants: For spasms associated with hip pain.
- Corticosteroids: Oral or injectable for severe inflammation.
- Disease-Modifying Drugs: For autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
2. Physiotherapy
- Strengthening exercises to improve hip stability and mobility.
- Stretching routines to reduce stiffness and increase flexibility.
- Heat and cold therapy to alleviate pain and swelling.
3. Interventional Pain Management
- Intra-Articular Injections:
- Corticosteroids for inflammation.
- Hyaluronic acid for joint lubrication in osteoarthritis.
- Nerve Blocks:
- For chronic hip pain, blocking specific nerves to reduce pain transmission.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA):
- Targeted heat therapy to deactivate nerves causing pain.
4. Regenerative Medicine
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP):
- Injected into the affected area to promote tissue healing.
- Stem Cell Therapy:
- Using healthy adult stem cells to regenerate damaged tissues and cartilage.
5. Surgical Interventions
Recommended for severe cases where non-surgical methods fail:
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to repair labral tears or remove bone spurs.
- Hip Replacement Surgery: Total or partial replacement for advanced arthritis or fractures.
Why Choose RS Pain Management Clinic?
- Non-Surgical Expertise: Focused on minimally invasive and regenerative treatments.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Utilizing cutting-edge imaging techniques for accurate diagnosis.
- Personalized Care: Tailored treatment plans for individual needs.
- Comprehensive Approach: Combining medical, interventional, and physiotherapy modalities.