Post-Herpetic Neuralgia (PHN) Treatment at RS Pain Management
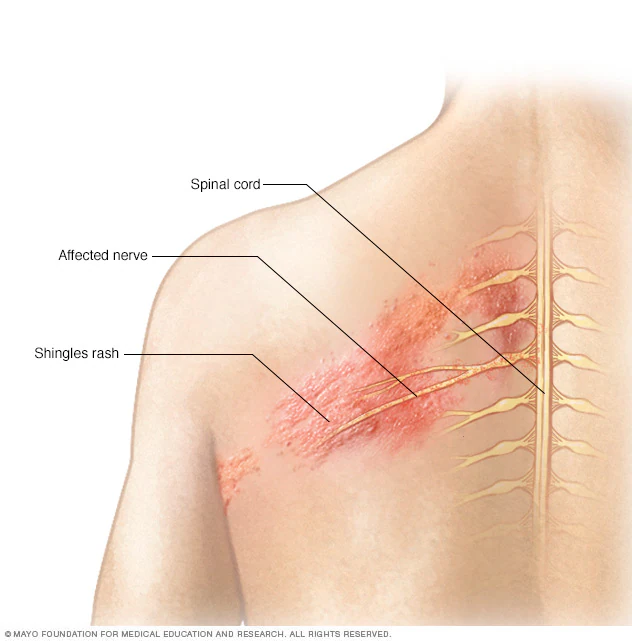
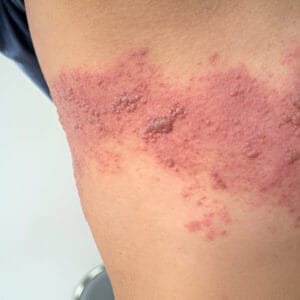
Post-Herpetic Neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic pain condition that occurs as a complication of shingles (herpes zoster). After the shingles rash heals, some individuals experience persistent pain in the affected area due to nerve damage caused by the varicella-zoster virus. PHN is one of the most challenging types of nerve pain, significantly affecting the quality of life.

Signs and Symptoms of PHN
- Burning, stabbing, or sharp pain in the area where the shingles rash was present.
- Allodynia (pain from stimuli that do not typically cause pain, such as light touch or clothing rubbing on the skin).
- Hyperalgesia (increased sensitivity to pain).
- Tingling, numbness, or itching.
- Persistent pain lasting for months or even years after the rash has resolved.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Nerve Damage: PHN develops when the shingles virus damages nerve fibers, causing the nerves to send exaggerated or incorrect pain signals to the brain.
- Age: Older adults, especially those over 60, are at higher risk.
- Severe Shingles: People with intense rash and pain during the shingles outbreak are more likely to develop PHN.
- Delayed Treatment: Delayed or untreated shingles can increase the likelihood of developing PHN.
Diagnosis
A detailed medical history and physical examination are conducted to evaluate the symptoms and the history of shingles. Diagnostic tools may include:
- Nerve Conduction Studies: To assess nerve function.
- Pain Mapping: Identifying the areas of sensitivity and pain intensity.
- Skin Biopsy or Imaging (in rare cases): To rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for PHN
Effective management of PHN aims to reduce pain, improve functionality, and enhance quality of life. At RS Pain Management, we use a combination of therapies to provide relief:
1. Medications
- Antidepressants: Amitriptyline, nortriptyline, or duloxetine to help regulate pain signals in the brain.
- Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin or pregabalin to reduce nerve excitability and alleviate pain.
- Topical Treatments:
- Capsaicin Cream: Helps desensitize nerve endings.
- Lidocaine Patches: Provide localized pain relief.
- Opioids (if necessary): Short-term use for severe pain under medical supervision.
- Steroids: To reduce inflammation and manage acute flare-ups.
2. Interventional Pain Procedures
- Nerve Blocks: Injection of anesthetic agents and steroids to block pain signals from the affected nerves.
- Epidural Injections: For cases with severe radiating pain.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Minimally invasive procedure to deactivate pain-transmitting nerves.
- Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS): Implantation of a device to disrupt pain signals sent to the brain.
3. Regenerative Medicine
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Stimulates nerve healing and reduces inflammation.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Promotes repair and regeneration of damaged nerve tissues.
4. Non-Invasive Therapies
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Uses low-voltage electrical currents to provide pain relief.
- Physiotherapy: Includes stretching, strengthening, and gentle exercises to maintain mobility and reduce discomfort.
5. Psychological Support
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps patients cope with the emotional and psychological toll of chronic pain.
- Relaxation Techniques: Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises.
Why Choose RS Pain Management?
- Comprehensive Approach: Combining medical, interventional, and regenerative treatments for optimal outcomes.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Using cutting-edge tools for precise identification of pain generators.
- Experienced Specialists: Expertise in managing complex nerve pain conditions like PHN.
- Compassionate Care: Personalized support and guidance throughout the treatment process.